What is Fascia? Ashley Black, Inventor of the FasciaBlaster, Weighs in
Understanding What Fascia is is a Pivotal Step in Advancing Fascia Science1

The Bottom Line: Fascia is Omnipresent in All the Spaces that Surround and Penetrate our Cells!

It is literally everywhere in the body!
In a nutshell, fascia is the connective tissue in the sense that it connects all our individual cells to one another. We have learned anatomy by viewing the body as “pieces” like the popular 80’s game, “Operation.” In the context of that game, fascia is in all the little spaces that our “parts” are NOT. It is essential to note that fascia is also not parts; it is all one system.
The NIH paper by Dr. ChungYang, MD3 describes fascia as an “uninterrupted viscoelastic tissue which forms a functional 3-dimensional collagen matrix3 and surrounds and connects every muscle and organ, forming continuity throughout the body.” Moreover, I like this general description.
Fascia can change states like water. 2 It can be highly viscous, almost liquid, or very rigid and strong. So, picture the human body, with trillions of little cells all placed in a “mold of the human body.” Now pour imaginary JelloTM Mix inside the human body mold with its trillions of cells being surrounded by the mix, circling and enveloping the little cells. When you remove the human body from the mold, the trillions of little cells will be held together by the viscous JelloTM Mix. The JelloTM will surround every single little cell of our make-believe JelloTM man. This is a much more accurate visual of what fascia is from a high-level, holistic standpoint.
Fascia is ultimately important for a multitude of reasons. Still, the most important thing to note about fascia is that it is ONE SYSTEM, like our nervous system or circulatory system, that surrounds and penetrates all the structures of the body. Like a giant sponge that cells are inlaid into. For more details on the “sciency” stuff on fascia, click here for the What is fascia Part 2 blog.
Ready for the drop-the-mic grand statement? OUR CELLS ARE FED, that’s right, fed their nutrition, energy, and oxygen BY THE FASCIA THAT SURROUNDS THEM. So, in essence, you can not have healthy cells without a healthy fascia system. I wholeheartedly believe that health is determined by one unified guiding principle: cell function. If cells function, we are well. If cells malfunction, we are sick. (Based on theories presented in Never Be Sick Again, a book by Raymond Francis)

Before I wrap my “general description” of fascia, I have one quick note. I would also argue that actual cells are made partially of fascia. This means that fascia also permeates the cell walls and, therefore, is the Extracellular and Intracellular continuum. This is still up for debate in Fasciology circles, but my opinion is that this is true.
Khans Academy describes this: “All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell and controls what goes in and comes out.” 4
So, it’s my authors' note that the fascia is the most important system of the body. I believe fascia is what connects us from the surface of our skin to the mitochondria matrix in one information-loaded, dynamic, and fractal system. When looking for answers for human health, performance, disease, emotions, and spiritual evolution, we should be looking at the fascia.
Finding Fascia
In a sea of confusion
Recently, fascia has become a buzzword with the success of the FasciaBlaster. If you Google fascia, you will see images of foam rollers and percussion guns that have absolutely nothing to do with regenerating fascia. And even worse, “fascia massagers,” what even is that? Most foam roller manufacturers and percussion gun makers don’t even claim to regenerate fascia, so why has the internet gone mad with disinformation in aggregate? Sadly, with this disinformation comes a gross misunderstanding of what fascia is and a railroading of the science of fascia that scientists have been fascinated with for hundreds, if not thousands of years.
Fascia is being called a “sheath” over muscles, and it’s only being associated with cellulite and stiffness, when this is, at best, a highly incomplete picture of what fascia is. With “Fascia Massagers” rising to an estimated $ 4 billion industry in the next few years, manufacturers are scrambling to monetize the trend and bandwagoning successful keywords.
So, it’s essential to me that fascia and Fasciology knowledge is properly circulated and the public is well informed. I am making it a personal mission not to let this vital science get lost in a sea of capitalism. Fascia knowledge is for everyone.
Modern Medicine And Google Are Confused
We are here to slay the truth for you!
Even the scientific community knows there is ambiguity out there. In this NIH study, researchers acknowledge that we have not yet arrived at a definition of fascia. 5 The white paper states:
“Researchers do not agree on one comprehensive "fascia" definition. Despite the scientific uncertainty, there is an agreement with medical text that the fascia covers every structure of the body, creating a structural continuity that gives form and function to every tissue and organ.”
So be very very wary of information and products that can’t cite peer-reviewed and published research about what fascia is, what it does, and how to address it.”

Fascia’s “Code Names” Help You See the Bigger Picture

Fascia has been described in many ways, and I can see how we got here. This is because fascia was basically just overlooked when the anatomy and physiology books were written. And it is still this way today. Fascia would appear in little glimpses of “pieces of anatomy” like plantar fasciitis or thoracolumbar fascia, but this is a gross misrepresentation of what the fascia really is.
You must learn to speak the crazy, backward language of modern medicine to even learn about fascia because fascia has secret code names. Fascia is also known as Membrane, Sheath, Aponeurosis, Connective tissue, Collagen fibers, Extracellular MATRIX, Arachnoid Mater, Pia Mater, Dura Mater, Tethered fibrous cords, Jellylike, Myofascial tissue, etc.
To say the least, missing fascia is one of human evolution’s biggest FUBARS. But I am here to clean it up, and I have devoted my life to studying fascia, Fasciology, and advancing treatments for preventive and regenerative fascia care.* Ok, rant over. Let’s move on to some more science.

Why is Fascia Important?
In a brief summary, Fascia is important because it is, in essence…lifeforce. Our bodies are a collection of trillions of cells that function together in mind, body, and soul as a collective energetic unit. Our cells are surrounded and permeated by fascia, which gives them life, literally.
Fascia is important because it is like the soil of our body, feeding the little plants that are our cells.
The soil that surrounds our growing cell roots. What would you do if a plant was wilting and headed for death? What would you do to breathe life into this precious plant? Would you do something to the plant, or would you address the soil that nourishes it? Most people would look at the quality of the soil. Fascia is what feeds our cells, like the soil to plants. And fascia doesn’t just feed our cells nourishment; it transfers energy.
I have much more to say about this, but I will save it for the next blog and go more in-depth. Don’t even get me started on the energetic possibilities.
Types of Fascia
To clear up the mass confusion around fascia, I identified and categorized, in my book, 4 types of fascia. But now I have a more complete picture of fascia and have decided to include a 5th.
1. Structural Fascia: Structural fascia runs in long stips like an Ace Bandage throughout the body. Tom Meyers and his work identifying “Anatomy Trains” has charted these layers of fascia the best I have ever seen. He describes how these continuous sheaths run at different depths throughout the body, encasing muscles. I always say there aren’t 600 muscles in the body; there is one muscle separated by fascia.
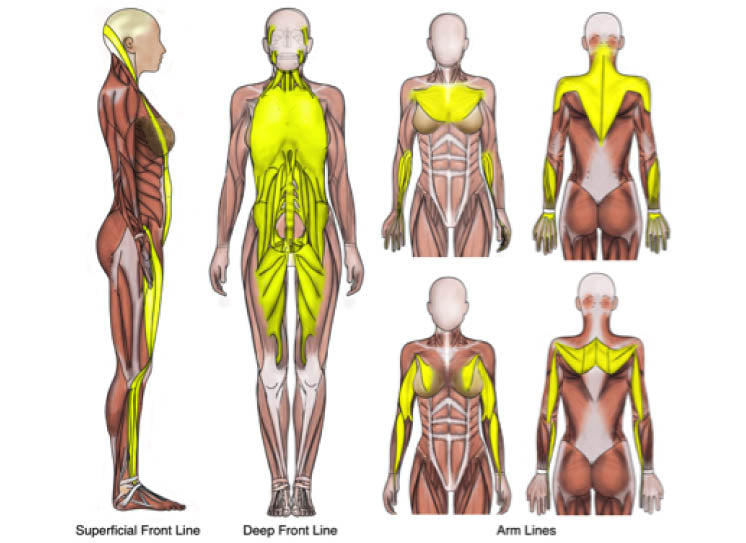
Ok, so I don’t love what is currently out there on the internet about superficial and deep fascia because this is an archaic way of defining fascia. Still, I will loosely throw them into the structural fascia category in case you encounter these definitions for structural fascia on the internet.
Superficial Fascia:
Some consider it the deepest layer of skin and the most surface layer of fascia. Superficial fascia gives your skin its outward appearance. The superficial fascia houses the stem cell reservoirs for the skin, and when palpated, it will release into the superficial fascia, smoothing skin6. Superficial fascia is sometimes called the outer bag.
Deep Fascia:
Deep fascia is referred to as any layer of fascia deeper than the skin. Layers of dense, fibrous connective tissue surround individual muscles and ligaments and group them for functional movement. The deepest layer is known as the periosteum. 1Deep fascia is sometimes called the inner bag.
2. Interstructural fascia: Fascia does not “just” surround muscles and other structures such as the heart and brain; it penetrates and permeates the cell. I love this video where I explain inter-structural fascia because it shows that each muscle fiber is surrounded by fascia, making up the inter-structural fascia. When we picture the 3D web of fascia, we can imagine fascia being pushed and pulled through all its individual parts permeated by inter-structural fascia.
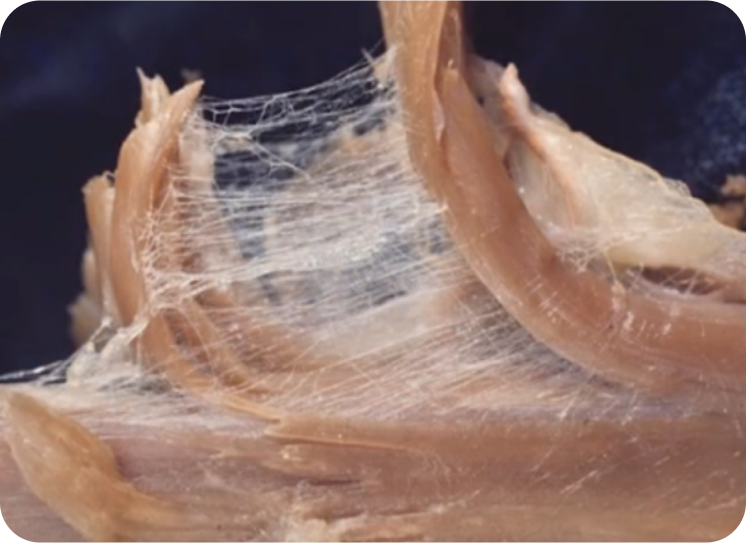

3. Visceral Fascia: If you've ever gutted a Turkey for Thanksgiving and seen the goopy, viscous mess inside, you’ve found your visceral fascia. Visceral fascia is usually associated with the abdomen. Visceral fascia surrounds your internal organs and suspends them in place.

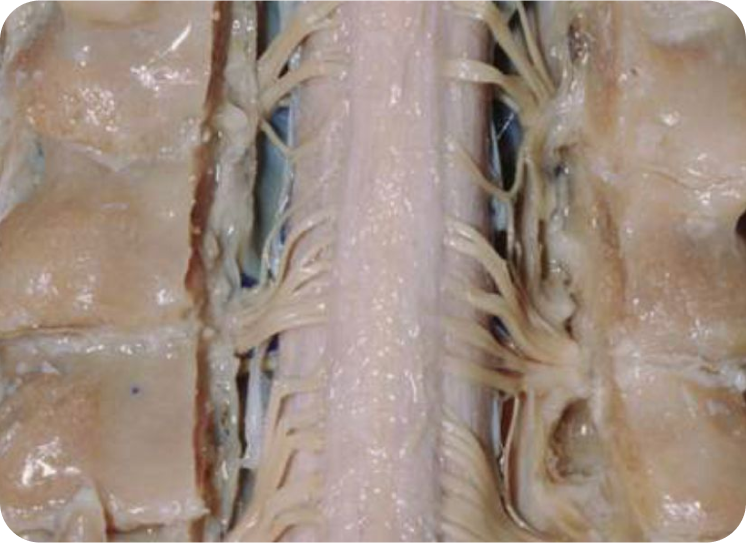
4. Fascial “Spinal Straw”: The three layers of fascia(dura mater, pia mater, and arachnoid mater) surround the spinal column and attach to all the other types of fascia to provide nourishment and hydration to the spinal discs of the spine. This type of fascia is also responsible for shortening the distance between vertebrae, causing damage to the disc. When this fascia is tight and narrow, we call that stenosis.
5. Viscous Fascia: This is the fascia I have been most fascinated with recently, and so have other scientists. Because fascia is made up of collagen and ground substance, it has the ability to be very dense and, I would argue, liquid. Most people know that collagen is a generous protein, but the ground substance is essential too, made up of Proteoglycans, GAGS (Glyco Amino Glycans), and water. Because of its liquidy, dense nature, it can reach the nooks and crannies around the cells.

I picture it like a giant sponge that sucks up nutrition and delivers it to the cells. When disturbed, 65-70% of this viscous gel-like fascia produces an electric charge, so it serves as a battery.
Together, the 5 types of fascia create quite the picture. Like a giant JelloTM man, with all our organs, bones, and muscles stuffed inside, long ace bandage strips running throughout, flowing like an ocean, producing an electrical charge. I revisit what I always say about fascia when asked: It’s lifeforce. For how this lifeforce works in detail, visit my What is Fascia Part 2 blog
With All Of This Knowledge Laid Out
We Created The Solution People Were Looking For.
If you made it this far, you probably want to know what you need to do to get or keep your fascia healthy. Remember that fascia is a system of the body; it is affected, like other systems of the body, by the food we eat, the amount of movement we experience, what medications we take, and whether we sleep well and manage stress. And, we can’t eliminate genetics (although this is the smallest influencing factor) or general lifestyle from the “healthy fascia” equation. How we move and the quality of our movement affects fascia. The body is one organism with the fascia affecting them all. So what we consume, including everything we consume, can cause the fascia to react. And fascia, like the rest of our body, likes detoxification, so how well we expel toxins affects the fascia.

Cited Works
2. Fascia and Primo Vascular System - PMC
3. Findley T. W. Fascia research from a clinician/scientist's perspective. International Journal of Therapeutic Massage & Bodywork. 2011;4(4):1–6.
4. Cell parts and functions (article) | Khan Academy
5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493
6. Shiseido Reveals Pressure Awakens Skin Regeneration Ability | NEWS RELEASE
* The Fasciablaster tools have not been cleared by the FDA for the treatment of any disease
Ashley Black, Inventor Of The Fasciablaster

Ashley Black is a decorated inventor, thought leader, and entrepreneur. She is best known for her work in the field of Fasciology. Fasciology is the study of the system of the body called fascia. Fascia is publicly known as the connective tissue, or web, that holds our body together, but fascia is also the viscous system that surrounds and feeds every cell in our bodies. Her work is directly related to the regeneration of this system of the body and the astounding effects this process can have on beauty, sports performance, and medical conditions.
She is best known for inventing instrument-assisted fascia techniques and tools, commercially known as FasciaBlasters. The tools entered the marketplace in 2014 and have become a household product. Black was the first person to write a #1 National Best Selling book about fascia, and she was the first person to do a TED Talk on fascia. By 2017-2018, her innovations and perseverance were rewarded with the American Business Association Stevie Award for Entrepreneur of the Year. IAOPT also awarded her with the Inventor of the Year. She also hit Inc's Fastest Growing Companies in America for the first time. This era was wrapped up with Ashley's self-reported highest accomplishment to date: the peer-reviewed Medical Publication of Research proving that FasciaBlasters can regenerate fascia tissue.
Since then, Ashley has received several awards, beginning with a second #1 National Best Selling Book about the struggles of females in business and authenticity in branding. She also received two global Stevie Awards from the International Business Association: Woman of the Year and a Lifetime Achievement Award for Consumer Goods.
In 2022, Ashley founded The Fascia Advancement Academy and the Fascia Advancement Charity to teach bodyworkers Fasciology. She has hit Inc's Fastest Growing Companies list for a second time, with over $150MM in revenue, profitable and growing. She boasts over 9 million social media followers and over 1 trillion unique media impressions for her work.





